How to model natural ventilation in Simergy?
Simple and detailed natural ventilation
There is a simple and a detailed natural ventilation option in Simergy. The simple approach is defined at the zone level and very flexible the detailed approach is using a network of nodes that all must be connected.
Simple natural ventilation
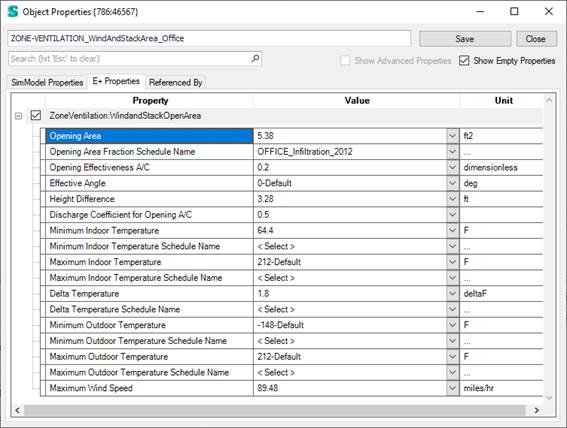
The simple natural ventilation is implemented in Simergy on a zone level with the EnergyPlus object: “ZoneVentilation:WindandStackOpenArea” (see documentation here: https://bigladdersoftware.com/epx/docs/9-2/input-output-reference/group-airflow.html#zoneventilationwindandstackopenarea). This simplified approach determines the ventilation air flow rate as a function of wind speed and thermal stack effect. This simple approach does not require anything else than this object to one or more thermal zones in the model. There is no interconnectivity.
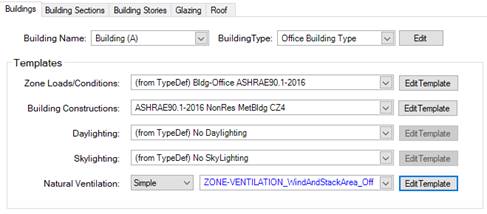
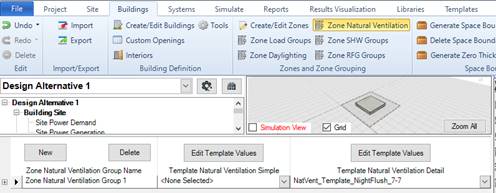
Defining natural ventilation templates
Both natural ventilation templates can be either defined at the building level (Building workspace -> Building tab) or via Zone Natural Ventilation groups. While for the simple natural ventilation only a library object is referenced for the detailed natural ventilation a template object is referenced.
Detailed natural ventilation
The detailed natural ventilation requires the specification of a NaturalVentilation Template object that defined NatVEnt controls, Zone Settings as well as possible cracks. In addition to this template opening properties can also be attached to windows and doors.
You need to define this node based detailed natural ventilation in a way that all nodes are connected. That means each zone that is assigned to a natural ventilation template must have at least two nodes (either opening or crack) and the resulting nodes must be connected.
Detailed about all related object and parameters can be found here: https://bigladdersoftware.com/epx/docs/9-2/input-output-reference/group-airflow-network.html#group-airflow-network
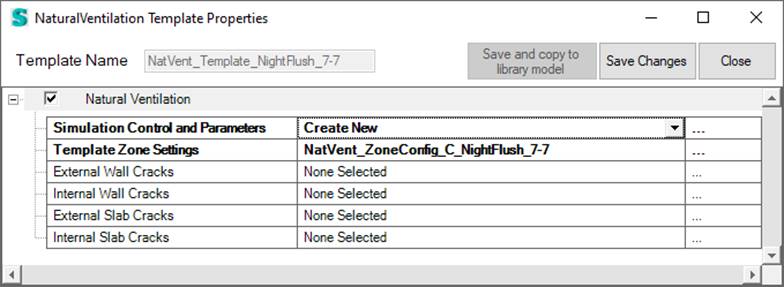
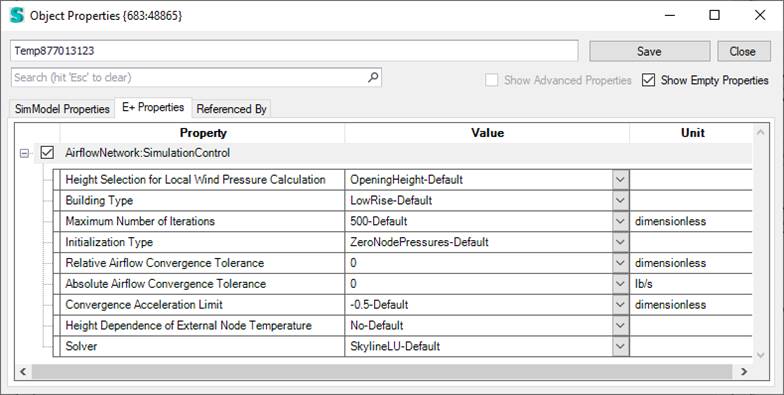
The basic run parameters for this model are defined in this unique simulation control object. Currently, in Simergy only the SurfraceAverageCalculation option for the wind pressure coefficients is supported.
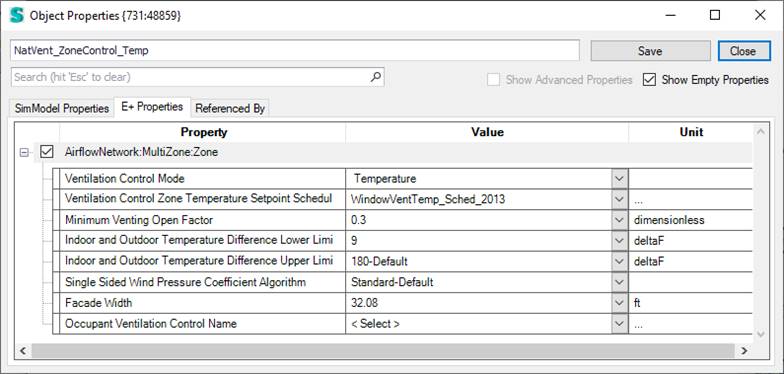
The AirflowNetwork:MultiZone:Zone object allows control of natural ventilation through exterior and interior openings in a zone, where “opening” is defined as an openable window or door.
This object is required to perform Airflow Network calculations. Note that ventilation control for all openings is provided at the zone level.
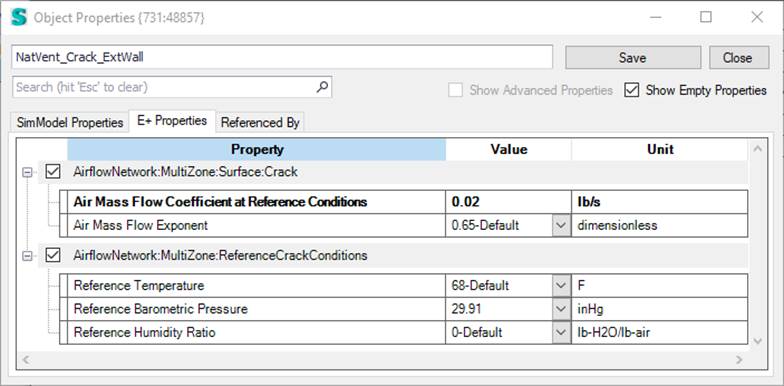
Different Opening types
There are 3 different opening types:
1. SimpleOpening
2. DetailedOpening
3. HorizontalOpening
Those opening properties are attached to windows or doors. You can use existing library entries by using Window or DoorTypes. Simergy is automatically generating AirFlowNetwork:Surface objects that related to these openings. Other air flow network objects in EnergyPlus are currently not supported in Simergy.
The SimpleOpening object specifies the properties of air flow through windows, doors and glass doors (heat transfer subsurfaces) when they are closed or open. The AirflowNetwork model assumes that open windows or doors are vertical or close to vertical.
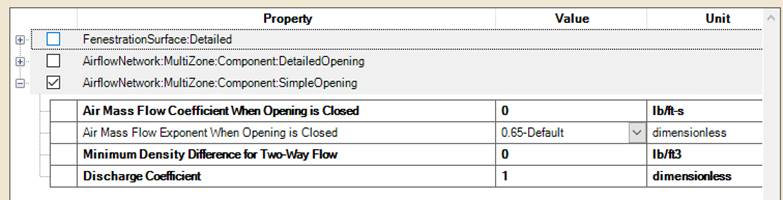
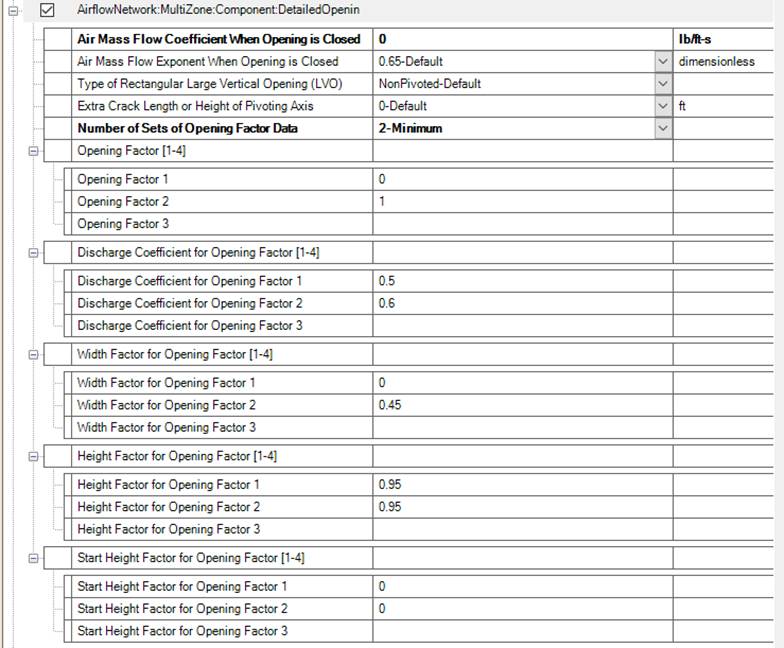
The DetailedOpening object specifies the properties of air flow through windows and doors (window, door and glass door heat transfer subsurfaces) when they are closed or open. The fields are similar to those for SimpleOpening object when the window or door is closed, but additional fields are required to describe the air flow characteristics when the window or door is open. These additional fields include opening type, opening dimensions, degree of opening, and opening schedule.
This object specifies the properties of air flow through windows, doors and glass doors (heat transfer subsurfaces defined as a subset of FenestrationSurface:Detailed objects) when they are closed or open. This AirflowNetwork model assumes that these openings are horizontal or close to horizontal and are interzone surfaces. The second and third input fields are similar to those for SimpleOpening/DetailedOpening when the window or door is closed, but additional information is required to describe the air flow characteristics when the window or door is open. This additional information is specified in the last two input fields. The airflow across the opening consists of two types of flows: forced and buoyancy. The forced flow is caused by the pressure difference between two zones, while the buoyancy flow only occurs when the air density in the upper zone is greater than the air density in the lower zone. This opening also allows for the possibility of two-way flow when forced and buoyancy flows co-exist.
